I. Intro
The FILTER function filters data based on conditions and returns the filtered data in the cell. It is useful for a wide range of applications for querying and analysis across various industries.
Arguments
FILTER(data range, filter condition)
- Range: A column or a set of data for which you want to filter. Tables or fields can be selected.
- Condition: The conditions for filtering the data within the selected range. Needs to be used in conjunction with CurrentValue.
Note: To use the FILTER function, you need to know how to reference data.
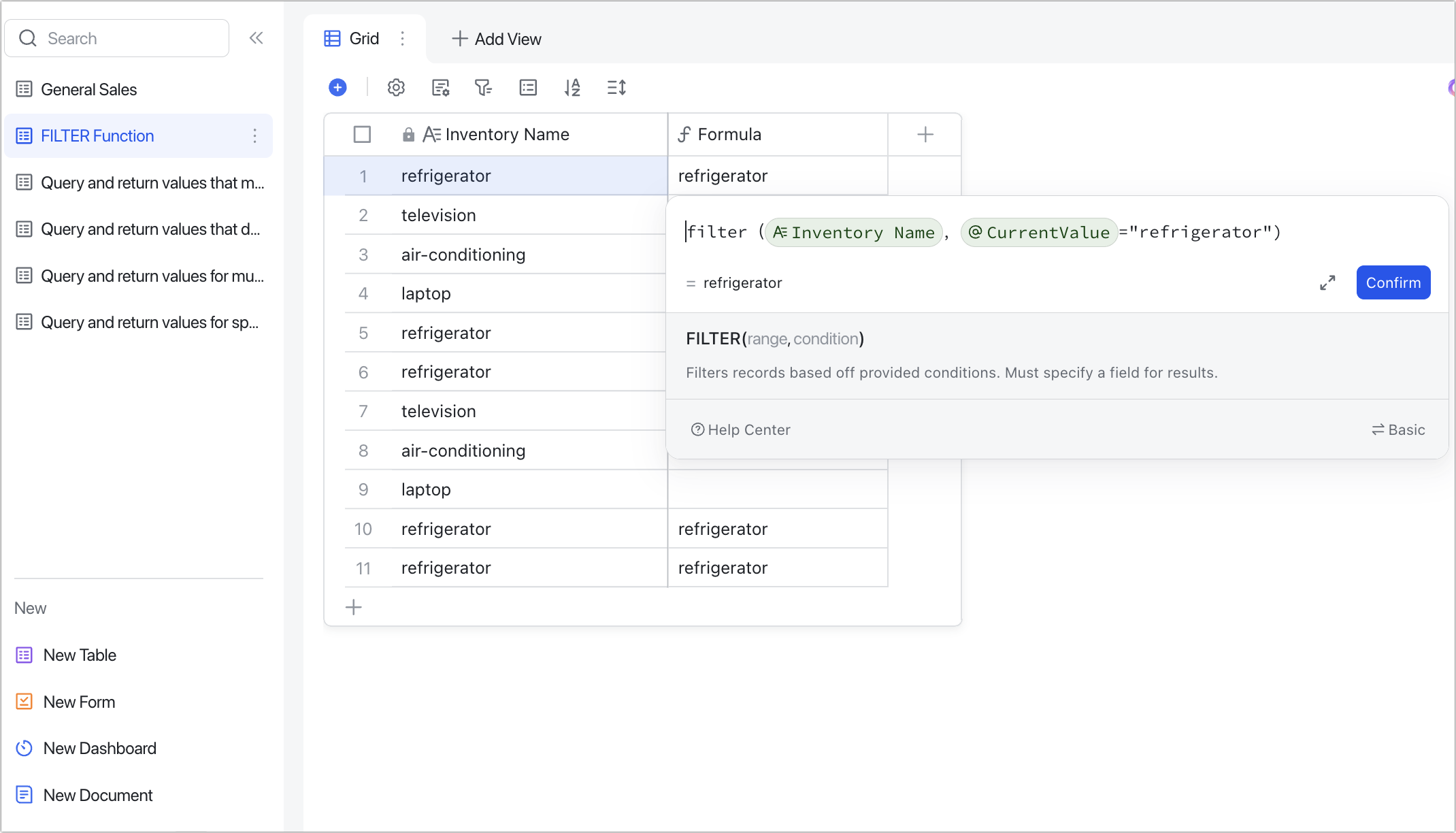
II. Steps
- Select a table, create a formula field, and enter the FILTER function. Set the range and condition as needed, and click Confirm.
250px|700px|reset
III. Use cases
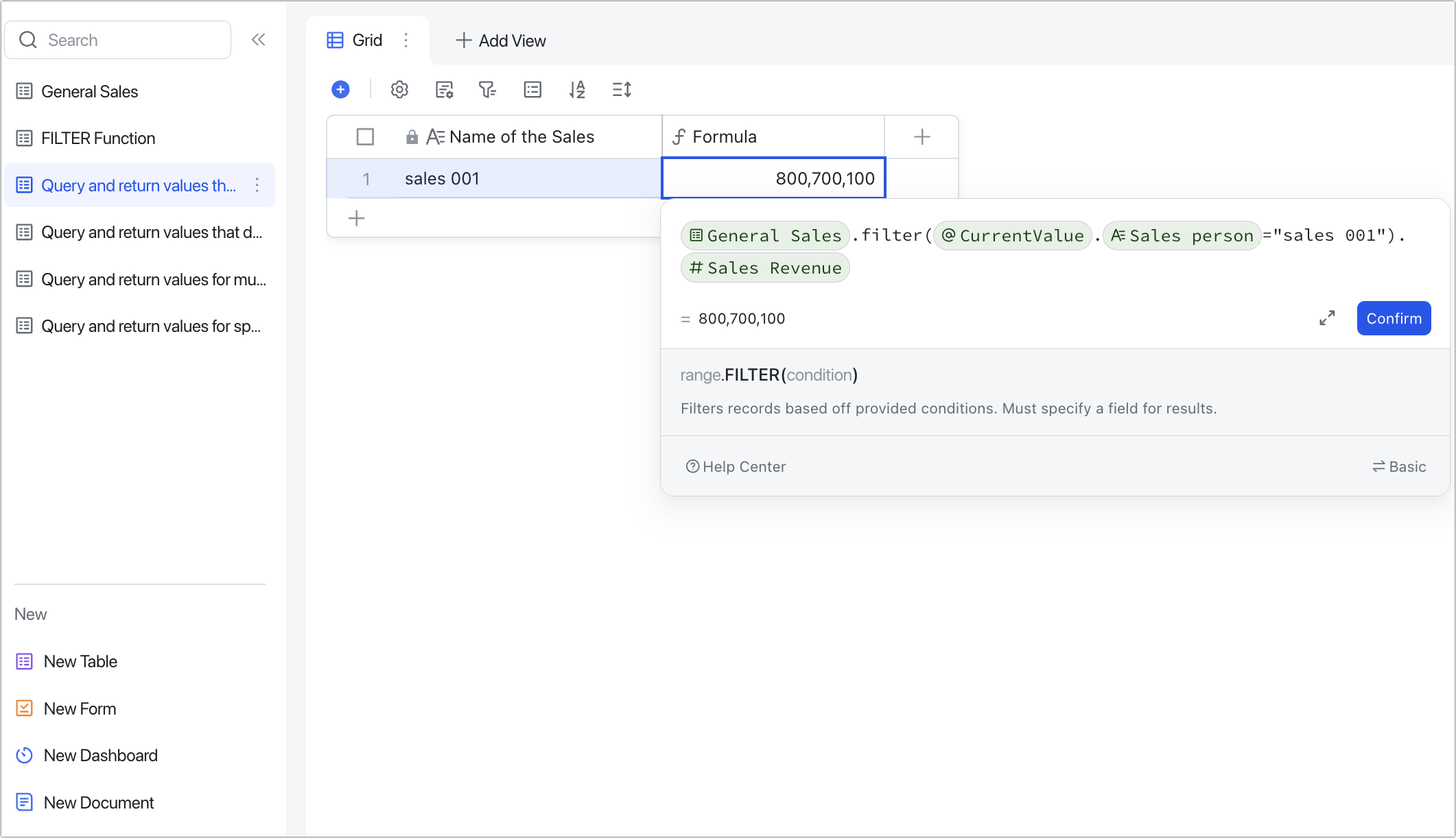
Query and return values that meet a specific value
Scenario: Querying the sales revenue of a salesperson.
Formulas: General Sales.FILTER(CurrentValue.Sales person="Sales 001").Sales Revenue
Explanation: Since the General Sales table is the data source that the FILTER function queries from, you need to refer to the field in that table for CurrentValue and not the field in the current table.
250px|700px|reset
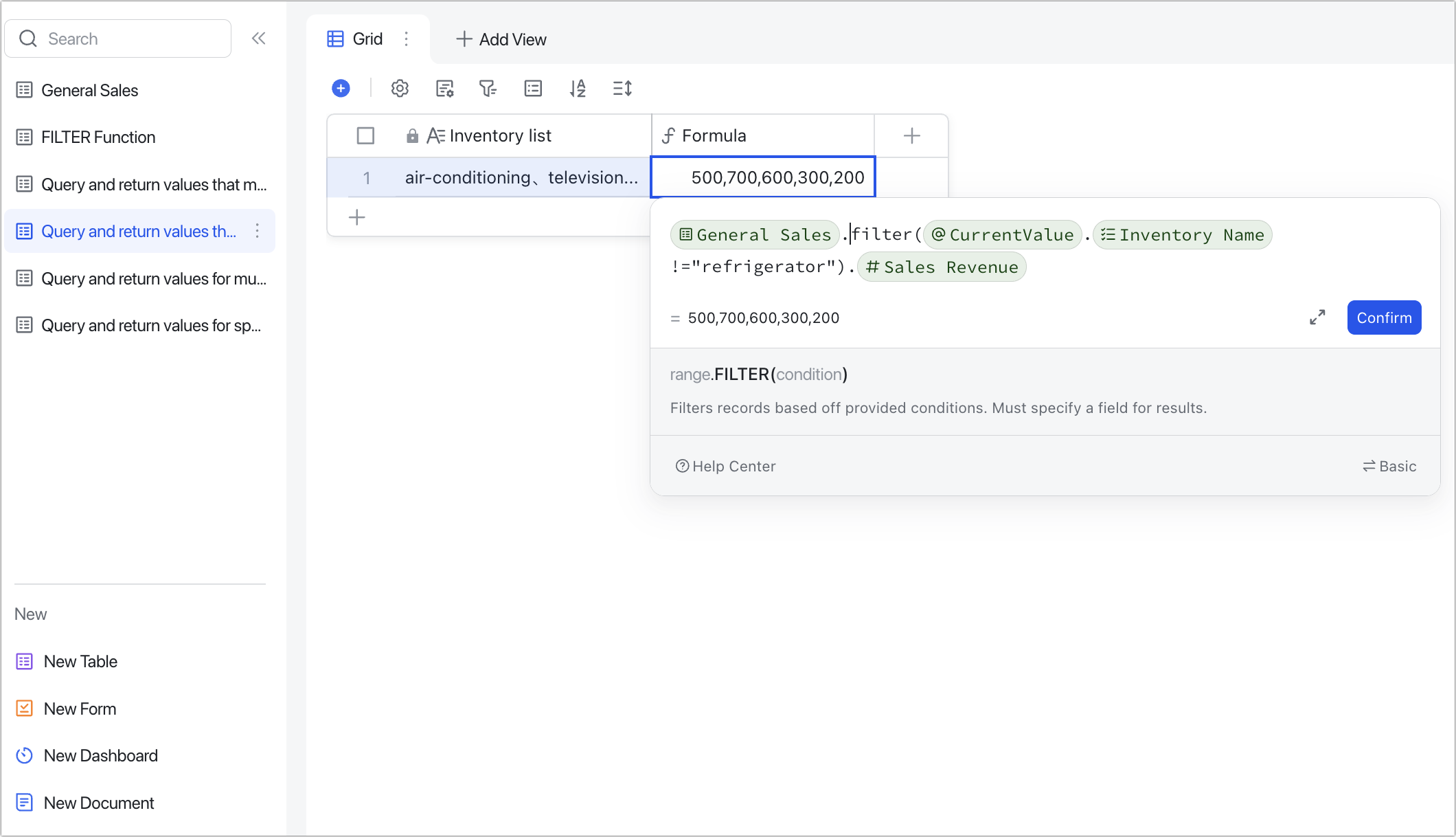
Query and return values that do not contain a specific value
Scenario: Querying the sales revenue of product types that are not refrigerators.
Formulas: General Sales.FILTER(CurrentValue.Inventory Name!="Refrigerator").Sale Revenues
Explanation: The != binary operators tell the function to look for values that do not match the specified value. When referencing fields for CurrentValue, use the field in the source table (General Sales).
250px|700px|reset
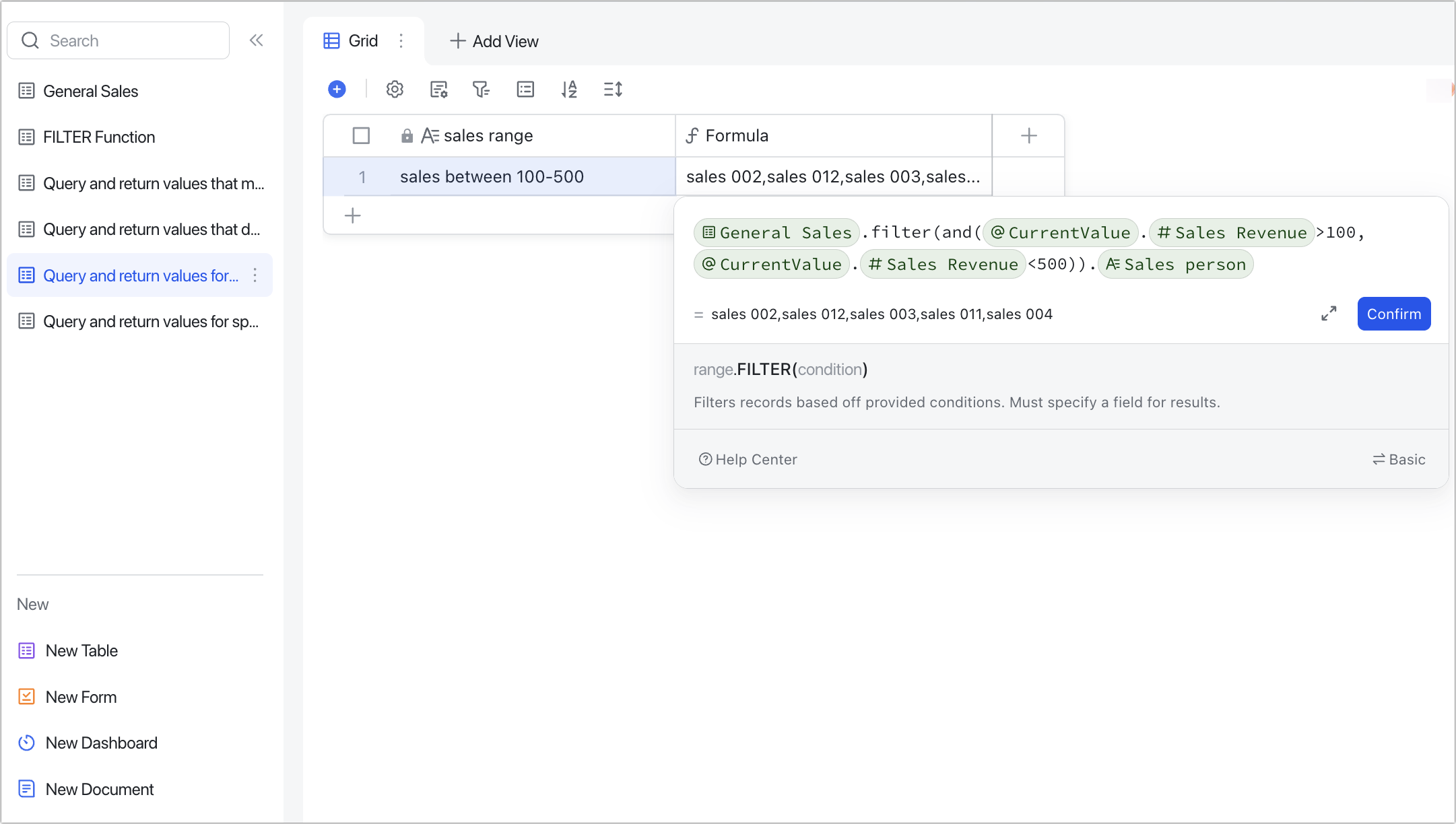
Query and return values that meet multiple conditions
Scenario 1: Filtering one variable. For example, querying sales people with sales between 100-500.
Formulas 1: General Sales.FILTER(AND(CurrentValue.Sales100,CurrentValue.Sales<500)).Salesperson
or Formulas 2: General Sales.FILTER(CurrentValue.Sales100 &&CurrentValue.Sales<500).Salesperson
Explanation: When filtering multiple conditions for one variable, you can use the AND() formula, or the binary operator && to represent the meaning of "and".
250px|700px|reset
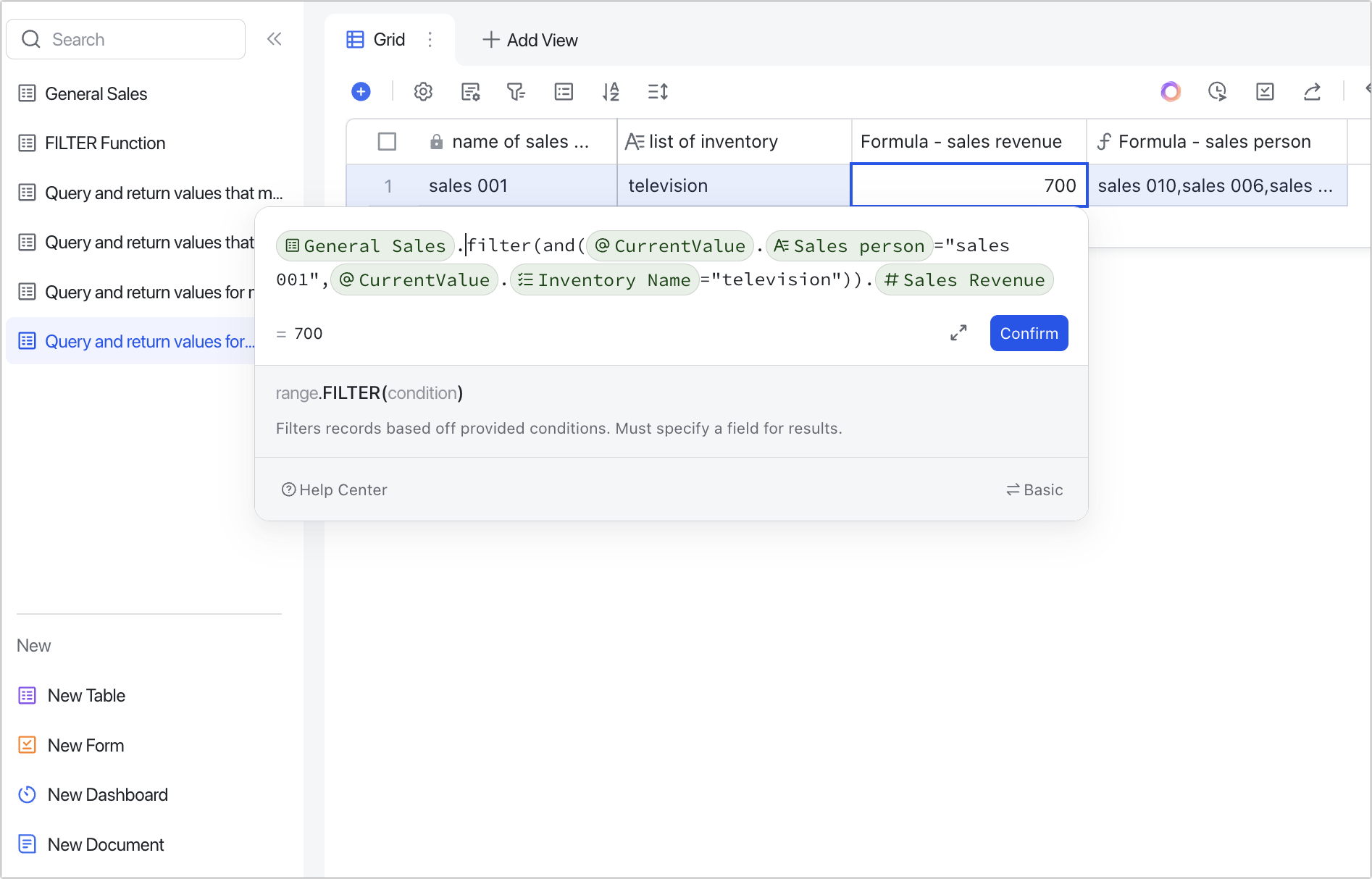
Scenario 2: Filtering multiple variables. For example, querying the sale revenue of TV for "Sales 001".
Formulas: General Sales.FILTER(AND(CurrentValue.Salesperson="Sales 001",CurrentValue.Inventory Name="TV")).Sales Revenue
Explanation: When filtering multiple conditions for multiple variables, you can nest the AND() function in the FILTER function to use the AND() function to require both conditions to be true.
250px|700px|reset
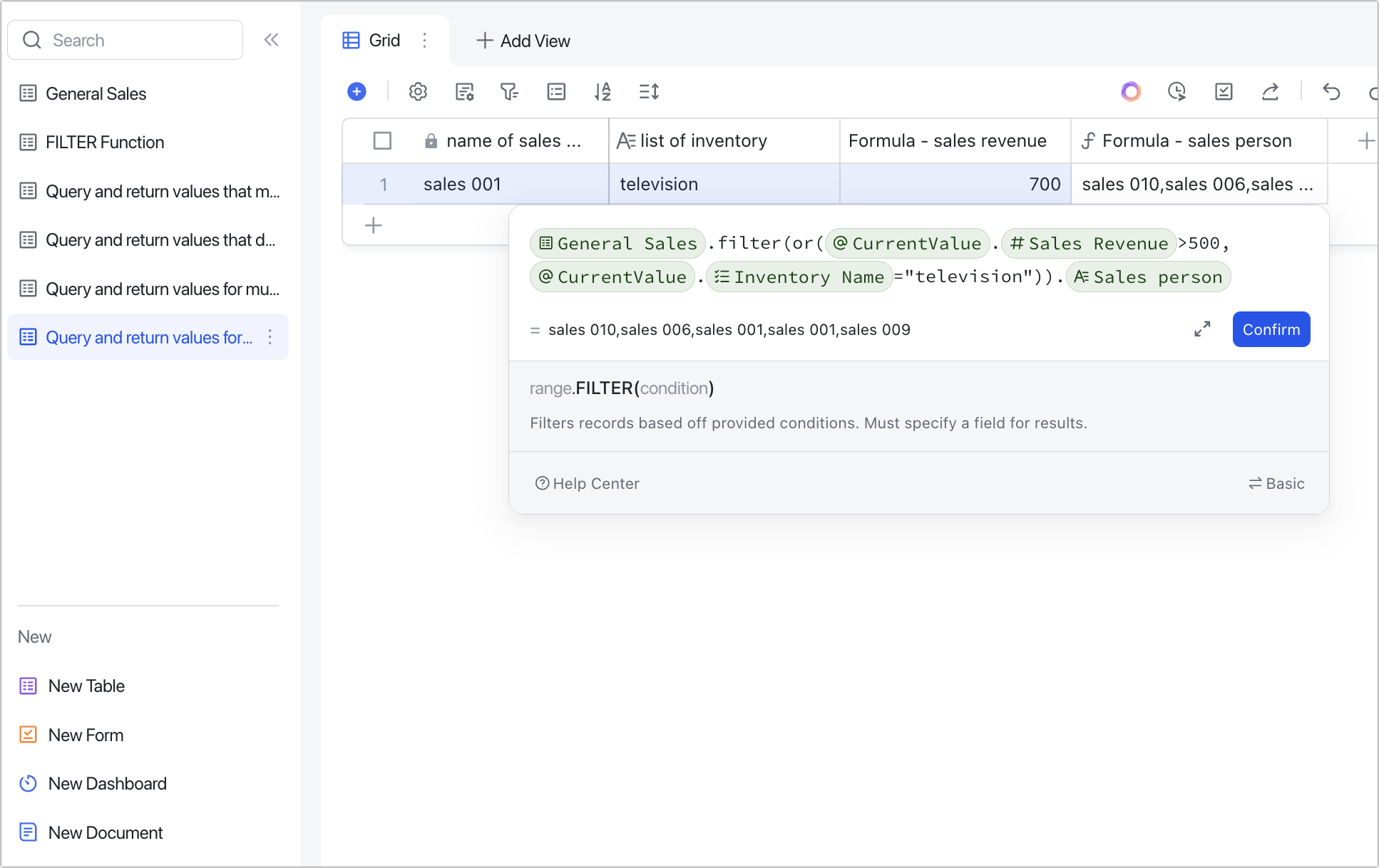
Scenario 3: Filtering multiple variables. For example, querying the salesperson with sales revenue greater than 500 or the product type is TV.
Formulas: General Sales.FILTER(OR(CurrentValue.Sales Revenue500,CurrentValue.Inventory Name="TV")).Salesperson
Explanation: When filtering multiple conditions for multiple variables, you can nest the OR() function in the FILTER function to use the OR() function to require only one option to be true.
250px|700px|reset
IV. FAQs

