Planning is the cornerstone of any successful project. Whether you’re leading a small startup or managing a large enterprise, having the right planning tools can make all the difference. From streamlining workflows to enhancing collaboration, these tools help teams stay organized and productive.
However, the needs of different teams vary significantly. A tool that’s perfect for a small team might lack the scalability required for a large organization. Similarly, tools designed for enterprises might be too complex or expensive for startups. Additionally, specific industries and scenarios call for tailored solutions.
This comprehensive guide explores the best planning tools for different team sizes and use cases. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of which tool is the best fit for your team.
Why Different Teams Need Different Planning Tools
One-size-fits-all tools don’t work for everyone
Every team has unique workflows, collaboration needs, and project complexities. Choosing the wrong planning tool can lead to inefficiencies, miscommunication, and wasted resources.
Small Teams: Typically require lightweight, cost-effective tools that are easy to set up and use. Collaboration and task management are key priorities.
Large Enterprises: Need scalable tools with robust features like advanced reporting, resource allocation, and integration with other enterprise systems.
Specialized Industries: Industries like construction, marketing, or creative design often require niche features tailored to their unique workflows.
By understanding your team’s specific needs, you can select a planning tool that enhances productivity and aligns with your goals.
Key Features of Excellent Planning Tools
What makes a planning tool great?
When evaluating planning tools, look for the following key features:
Collaboration Features: Tools should enable real-time updates, shared dashboards, and seamless communication.
Scalability: The ability to adapt as your team grows or your projects become more complex.
Integration: Compatibility with tools like Slack, Google Workspace, or CRM systems ensures smooth workflows.
Customization: Tailored workflows, templates, and dashboards help teams adapt tools to their specific needs.
Flexible Pricing: Free plans for small teams and affordable upgrades for growing organizations.
What features should your team prioritize?
The dimensions to focus on are different for different types of businesses. You can focus on picking the tools that are more suitable for your type of business.
Startups and Small Companies: Focus on affordability, ease of use, and collaboration features.
Large Enterprises: Prioritize integration capabilities, advanced reporting, and customization to handle complex workflows.
Specialized Industries: Look for tools with industry-specific features, such as resource planning for construction or brainstorming templates for creative teams.
To provide a clearer comparison of the different planning tools, we have evaluated 10 tools across five key dimensions: Collaboration Features, Scalability, Integration, Customization, and Flexible Pricing. Each tool is rated on a score of 1 to 5 , where 5 indicate exceptional performance and 1 indicates weaker performance. Below is the rating table:
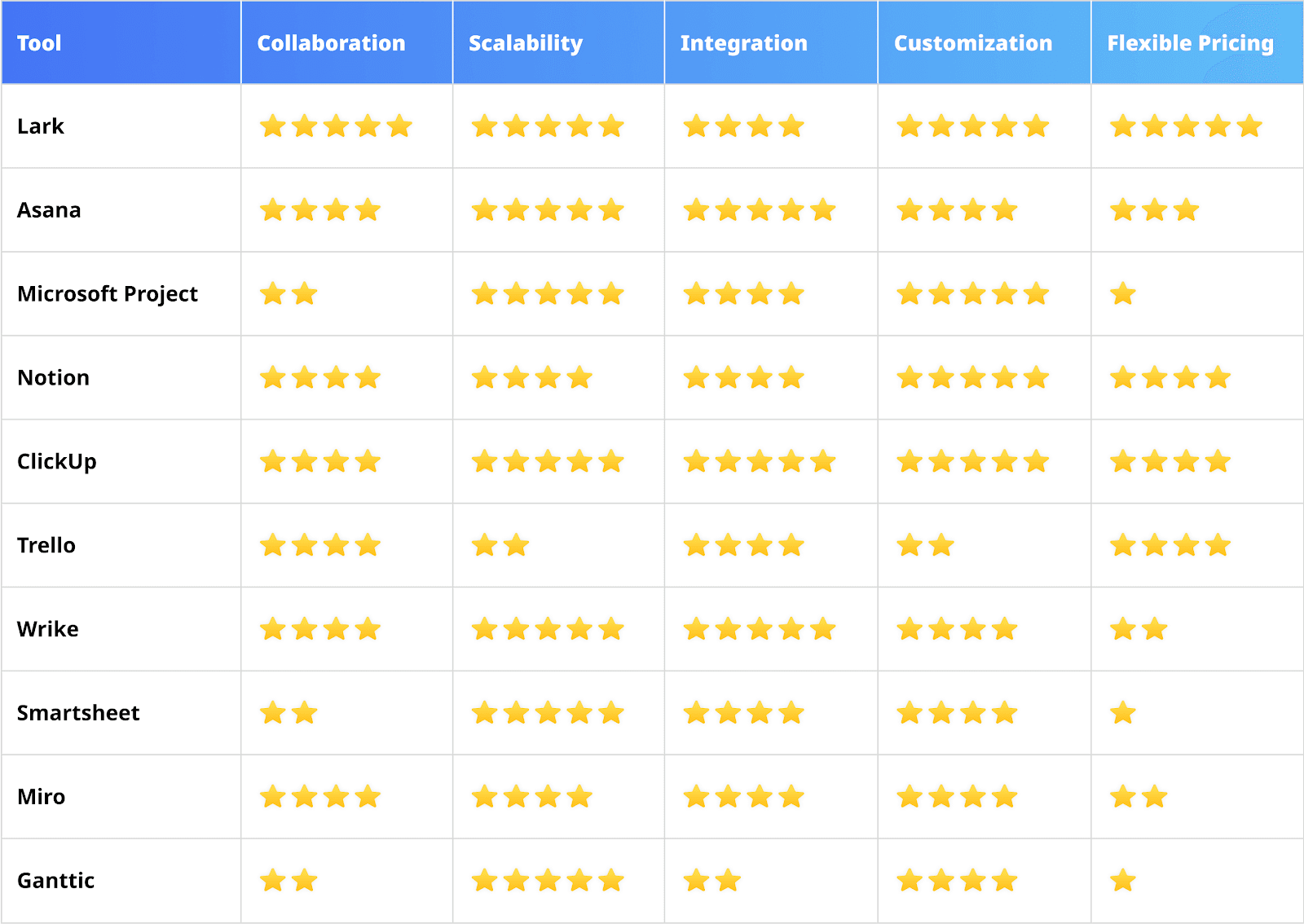
Rating Explanation:
5 Stars: Outstanding performance, comprehensive features, and meets the needs of most teams.
4 Stars: Excellent performance with strong features, but may have minor shortcomings in certain areas.
3 Stars: Good performance, suitable for specific scenarios, but with limited functionality or flexibility.
2 Stars: Average performance, with basic features or noticeable limitations.
1 Star: Poor performance, lacking essential features or offering low value for money.
Pros and Cons of Tools for Different Team Sizes
1. Lark
Lark integrates messaging, video calls, cloud storage, and collaborative documents into one platform. It’s designed for agile teams needing real-time communication, streamlined workflows, and powerful integrations, making it ideal for startups and fast-paced organizations managing dynamic projects.
Small Teams:
Pros: Lark offers a free plan with a user-friendly interface that integrates chat, calendar, and task management into one platform. Its Base feature allows small teams to create Gantt charts, dashboards, and visualized workflows, making it easy to plan and track projects. The ability to embed plans into documents for real-time editing and brainstorming is a standout feature.
Cons: As an all-in-one tool, Lark works best when used alongside its suite of products. Teams already using other tools may face challenges migrating or integrating.
Recommended Use Case:
Agile Product Teams: Lark is perfect for small, fast-moving teams that need real-time updates and seamless communication. For example, a startup developing a mobile app can use Lark to manage sprints, track progress, and collaborate on product roadmaps. In addition, Lark also provides rich template resources for business scenarios for more teams.
Large Teams:
Pros: Lark scales well for cross-department communication and collaboration. Its integration of chat, video calls, and task management ensures that large teams stay connected and aligned.
Cons: Advanced planning needs may require additional integrations or customizations.
Use Case:
Knowledge-Based Projects: Large teams working on research or knowledge-sharing projects can benefit from Lark’s ability to centralize communication and documentation. For instance, a multinational consulting firm can use Lark to manage client deliverables, share insights, and coordinate across global offices.
Content Teams: Content creators and editors can use Lark’s Base feature to plan editorial calendars, assign tasks, and track deadlines, all while collaborating in real-time on shared documents.
Content Teams: Content creators and editors can use Lark’s Base feature to plan editorial calendars, assign tasks, and track deadlines, ensuring everyone stays aligned. For large teams, where information gaps can easily occur, Lark’s real-time collaboration tools, such as shared documents and comments, enable seamless communication and ensure that updates, feedback, and progress are accessible to everyone, minimizing miscommunication and enhancing efficiency.
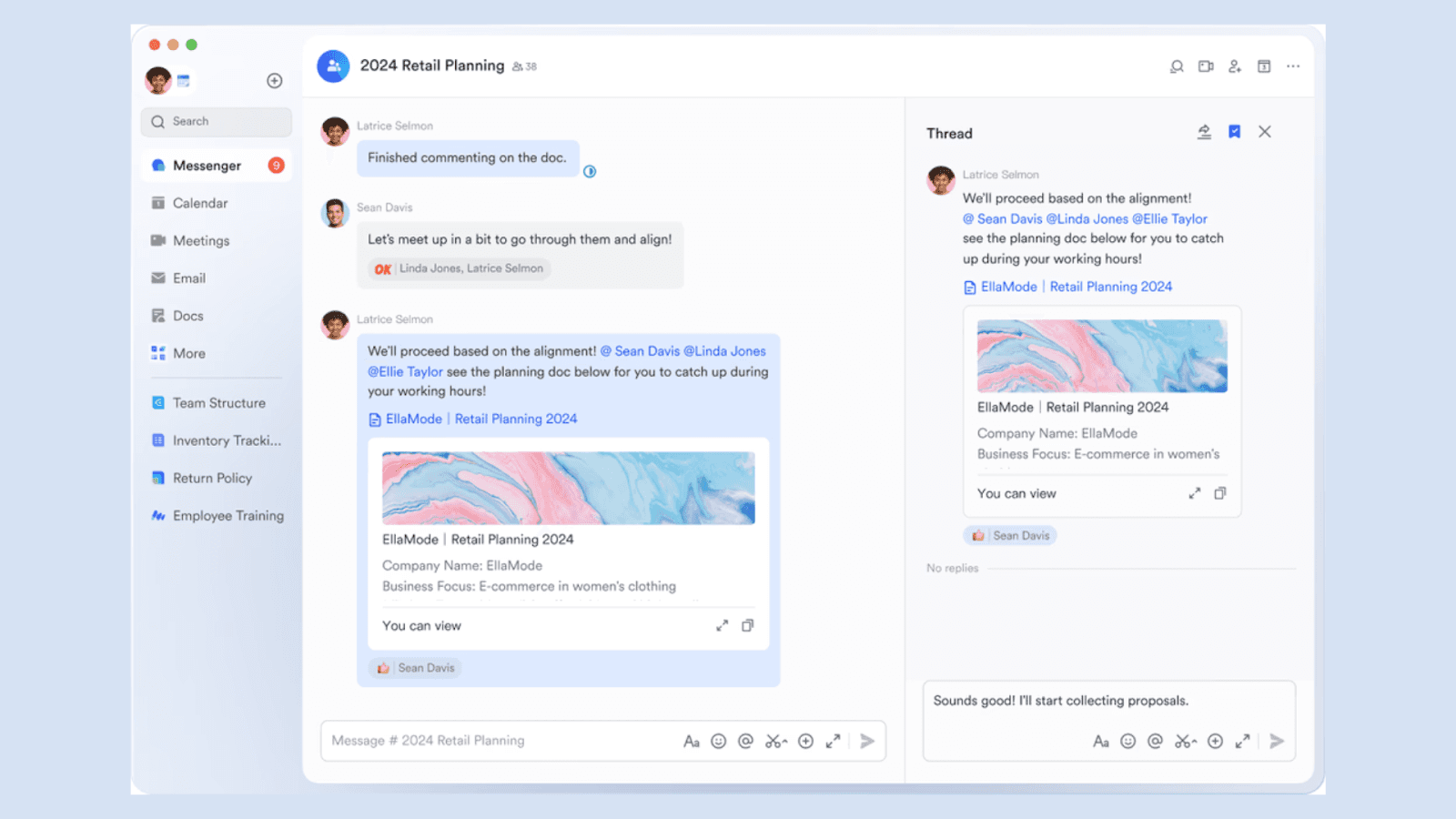
Image source: lark.com
2. Asana
Asana helps teams organize tasks, set priorities, and track progress with features like timelines and workflow automation. It’s particularly effective for medium to large teams managing cross-functional projects, ensuring clarity and accountability across all stages of work.
Small Teams:
Pros: Asana simplifies task assignments, deadlines, and project tracking, making it ideal for small teams. Its free plan includes essential features like task lists, boards, and calendar views.
Cons: For very small or simple projects, Asana’s features may feel excessive or overwhelming.
Recommended Use Case:
Marketing Campaigns: A small marketing agency can use Asana to plan campaigns, assign tasks to team members, and track deliverables. For example, a team launching a social media campaign can use Asana’s timeline view to visualize deadlines and dependencies.
Large Teams:
Pros: Asana’s advanced features, such as timeline views, workload management, and custom fields, make it scalable for enterprise use.
Cons: Higher-tier pricing plans can be expensive for large organizations.
Use Case:
Cross-Functional Projects: Large enterprises managing cross-functional projects, such as product launches, can use Asana to align teams, track progress, and ensure accountability. For instance, a tech company launching a new software product can use Asana to coordinate between engineering, marketing, and sales teams.
Image source: asana.com
3. Microsoft Project
Microsoft Project is a professional-grade tool for planning, scheduling, and resource management. With advanced Gantt charts and budgeting capabilities, it’s tailored for enterprises handling large-scale, complex projects that require detailed oversight and precise execution.
Small Teams:
Pros: Microsoft Project provides comprehensive planning features for structured projects, including Gantt charts and resource management.
Cons: Its steep learning curve and high costs make it less suitable for small teams with limited budgets.
Use Case:
Construction Projects: A small construction firm can use Microsoft Project to plan timelines, allocate resources, and track progress on building projects. For example, a team managing a residential construction project can use the tool to schedule tasks and monitor dependencies.
Large Teams:
Pros: Microsoft Project offers enterprise-level project management with advanced resource allocation, reporting, and integration with other Microsoft tools.
Cons: Complexity and training requirements may slow adoption.
Use Case:
Enterprise Resource Planning: Large organizations managing multiple projects simultaneously can use Microsoft Project to allocate resources efficiently and generate detailed reports. For instance, a global manufacturing company can use the tool to manage production schedules across multiple facilities.
Image source: microsoft.com
4. Notion
Notion offers a flexible workspace for managing tasks, notes, and databases. Its customizable templates and modular design make it ideal for individuals and teams looking to centralize project planning, knowledge sharing, and creative brainstorming in one intuitive platform.
Small Teams:
Pros: Notion combines knowledge management and planning, offering a highly customizable platform for small teams.
Cons: It lacks task-specific features for managing complex workflows.
Use Case:
Creative Teams: A small design studio can use Notion to brainstorm ideas, organize project assets, and track client feedback. For example, a team working on a branding project can create a shared workspace to store mood boards, design drafts, and project timelines.
Large Teams:
Pros: Notion is great for documentation and cross-team collaboration, allowing large teams to centralize knowledge and workflows.
Cons: Without clear organization, Notion workspaces can become cluttered.
Use Case:
Knowledge Management: Large teams in industries like consulting or education can use Notion to create centralized knowledge hubs. For instance, a university department can use Notion to store research papers, meeting notes, and project plans.
Image source: notion.com
5. ClickUp
ClickUp is a highly customizable productivity tool that combines task management, goal tracking, and collaboration features. It’s suitable for teams of all sizes, offering flexibility to adapt workflows for diverse industries and project types, from software development to marketing.
Small Teams:
Pros: ClickUp’s free plan offers robust features, including task management, time tracking, and goal setting.
Cons: Its extensive features can feel overwhelming for very small teams.
Pros: ClickUp’s free plan is feature-rich for personal use, offering tools like task management, time tracking, and goal setting, making it ideal for individuals managing their own projects.
Cons: The free plan lacks team creation capabilities, limiting its use for collaborative work. Additionally, its extensive features can feel overwhelming for very small teams or new users.
Use Case:
Freelancers and Startups: Freelancers or small startups can use ClickUp to manage client projects, track deadlines, and set goals. For example, a freelance web developer can use ClickUp to organize tasks for multiple clients and monitor progress.
Large Teams:
Pros: ClickUp’s all-in-one platform includes advanced features like automation, custom dashboards, and integrations.
Cons: Requires setup and training to fully utilize.
Use Case:
Product Development: Large product teams can use ClickUp to manage backlogs, plan sprints, and track releases. For instance, a software development team can use ClickUp to coordinate between developers, designers, and QA testers.
Looking for more products similar to ClickUp? Click to view ClickUp alternatives.
Image source: clickup.com
6. Trello
Trello uses a simple, visual Kanban board system to help teams organize tasks and workflows. Its intuitive drag-and-drop interface makes it perfect for small teams or individuals managing straightforward projects, with integrations to enhance productivity.
Small Teams:
Pros: Trello’s simple Kanban boards are easy to use and free for basic features.
Cons: Limited scalability and advanced features for complex projects.
Use Case:
Task Prioritization: A small team managing daily tasks can use Trello to organize to-do lists and prioritize work. For example, a content team can use Trello to track blog post ideas, drafts, and publishing schedules.
Large Teams:
Pros: Trello can manage multiple boards for different teams.
Cons: Lacks built-in reporting and resource management tools.
Use Case:
Departmental Workflows: Large organizations can use Trello to manage workflows within individual departments. For instance, an HR team can use Trello to track recruitment pipelines and onboarding processes.
Image source: trello.com
7. Wrike
Wrike is a collaborative project management tool offering features like workload balancing, custom dashboards, and real-time updates. It’s ideal for medium to large teams needing detailed project tracking and seamless collaboration across departments or remote teams.
Small Teams:
Pros: Wrike offers customizable workflows and a free plan for small teams.
Cons: Overly complex for simpler projects.
Use Case:
Event Planning: A small event planning team can use Wrike to manage timelines, assign tasks, and track budgets. For example, a team organizing a corporate conference can use Wrike to coordinate with vendors and monitor deadlines.
Large Teams:
Pros: Wrike scales well with robust reporting and time-tracking features.
Cons: Advanced features require higher-tier pricing.
Use Case:
Marketing Campaigns: Large marketing teams can use Wrike to manage multiple campaigns simultaneously. For instance, a global brand can use Wrike to coordinate regional marketing efforts and track campaign performance.
Image source: wrike.com
8. Smartsheet
Smartsheet combines spreadsheet simplicity with advanced project management tools like automation and reporting. It’s well-suited for teams managing data-heavy projects, providing a structured yet flexible way to plan, track, and execute tasks efficiently.
Small Teams:
Pros: Smartsheet’s spreadsheet-like interface is familiar and easy to use.
Cons: Limited collaboration features compared to other tools.
Use Case:
Budget Tracking: A small finance team can use Smartsheet to track budgets and expenses. For example, a nonprofit organization can use Smartsheet to monitor grant spending and generate reports.
Large Teams:
Pros: Smartsheet supports automation and scalability for managing multiple projects.
Cons: Can become complex with larger datasets.
Use Case:
Project Portfolios: Large organizations managing multiple projects can use Smartsheet to track progress and allocate resources. For instance, a construction company can use Smartsheet to oversee multiple building projects.
Image source: smartsheet.com
9. Miro
Miro is an online collaborative whiteboard designed for brainstorming, planning, and visualizing ideas. It’s perfect for remote teams and creative professionals who need an interactive space for ideation, strategy development, and real-time collaboration.
Small Teams:
Pros: Miro’s visual collaboration tools are perfect for brainstorming and planning.
Cons: Limited project management features beyond brainstorming.
Use Case:
Creative Workshops: A small creative team can use Miro to brainstorm ideas and map out strategies. For example, a design team can use Miro to create mood boards and wireframes for a new website.
Large Teams:
Pros: Miro is great for strategic planning and cross-team collaboration.
Cons: May require integration with other tools for full project management.
Use Case:
Strategic Planning: Large organizations can use Miro to facilitate strategic planning sessions. For instance, a multinational corporation can use Miro to map out long-term goals and align teams across regions.
Image source: miro.com
10. Ganttic
Ganttic specializes in resource planning and scheduling, helping teams optimize workloads and allocate resources effectively. It’s particularly useful for industries like engineering or manufacturing, where balancing capacity and project timelines is critical to success.
Small Teams:
Pros: Ganttic focuses on resource planning, making it ideal for resource-heavy projects.
Cons: Narrow focus, lacks task management features.
Use Case:
Resource Allocation: A small engineering team can use Ganttic to allocate resources and track availability. For example, a team working on a product prototype can use Ganttic to schedule equipment usage and monitor team workloads.
Large Teams:
Pros: Ganttic is ideal for resource-heavy industries like construction or manufacturing.
Cons: Not suitable for broader project management.
Use Case:
Industrial Projects: Large teams in industries like construction can use Ganttic to manage resources across multiple projects. For instance, a construction company can use Ganttic to schedule machinery and labor for various building sites.
Image source: ganttic.com
How to Choose the Right Planning Tool for Your Team
Match tools to your needs
Evaluate tools based on team size, budget, and workflow complexity.
Test tools through free trials or demos.
Consider tools like Lark, which offer free trials and onboarding support.
Why choose Lark?
Collaboration: Lark stands out with its robust collaboration capabilities, integrating chat, video conferencing, task management, and document collaboration with real-time editing and sharing. These all-in-one features outperform most tools, especially Microsoft Project and Ganttic, which lack strong collaboration functionalities.
Scalability: Lark offers exceptional scalability, making it suitable for both small teams and large, cross-departmental organizations. It is particularly ideal for knowledge-based projects and agile teams. In contrast, tools like Trello and Notion may face limitations when used by larger teams.
Integration: Lark integrates seamlessly with tools like Google Workspace and Slack, while also supporting a wide range of third-party applications. Its integration capabilities are comparable to those of Asana and ClickUp.
Customization: Lark provides flexible workflows and templates, allowing deep customization of Gantt charts, dashboards, and Base features, making it adaptable to various work scenarios. In comparison, Trello and Smartsheet offer more basic customization options.
Conclusion
The right planning tool can transform the way your team collaborates, plans, and executes projects. Rather than a one-size-fits-all solution, the tools in this guide cater to diverse team sizes, industries, and workflows. Whether you’re a startup looking for simplicity or an enterprise needing robust features, selecting a tool aligned with your goals ensures efficiency and long-term success. Take the time to evaluate your team’s unique needs and leverage the strengths of tools like Lark, Asana, or Microsoft Project to unlock your team’s full potential.








